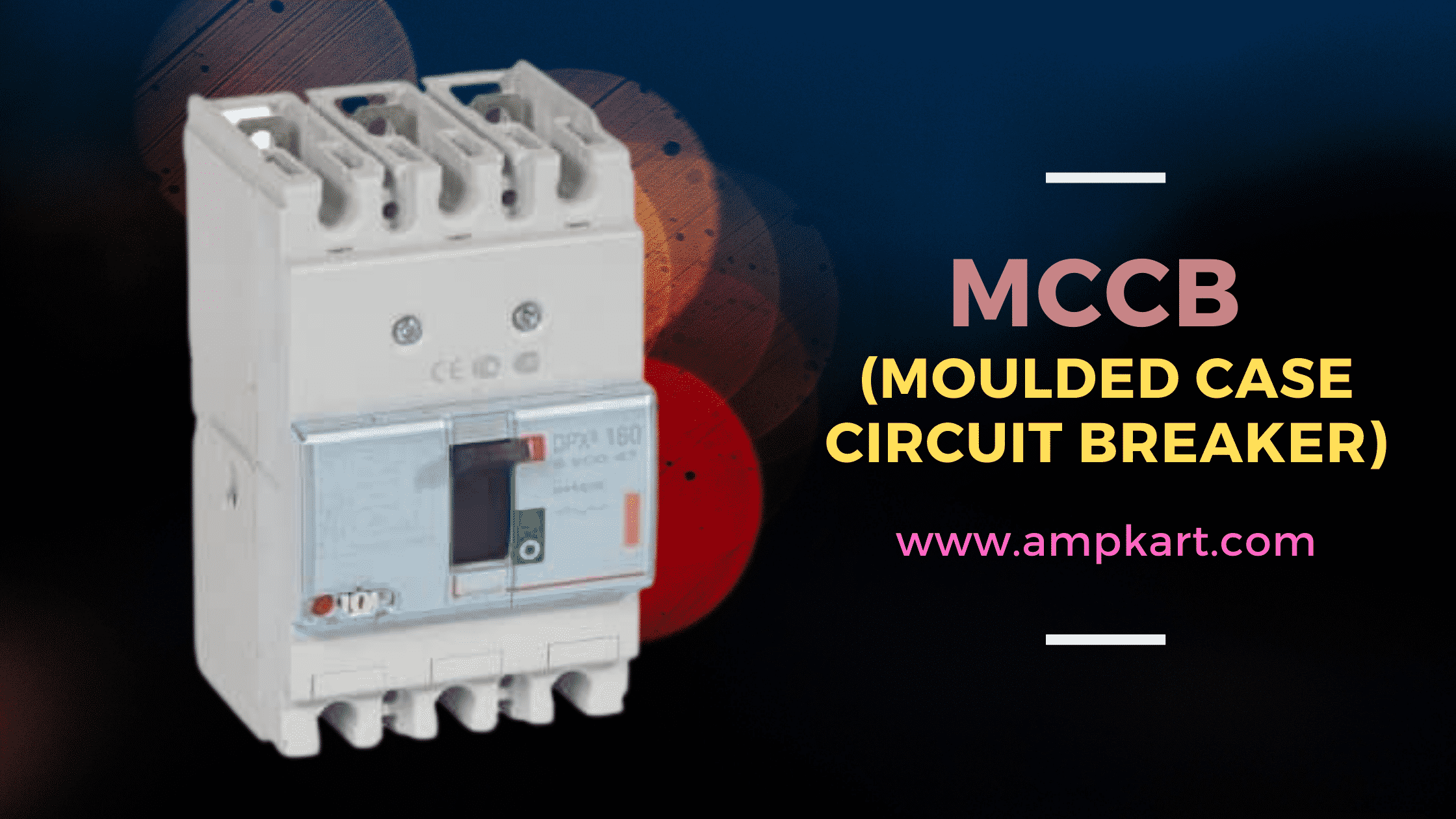
MCCBs are automated electrical devices that protect electrical appliances from overloads, short circuits, instantaneous overcurrents, and earth faults. It’s a more sophisticated version of MCB. The key benefit of an MCCB (Moulded Case Circuit Breaker) is that it can be customized to meet our needs by adding new features such as remote closing, UV ride, and so on.
-
 ABB MCCB 25kA₹2,605 – ₹3,531
ABB MCCB 25kA₹2,605 – ₹3,531
-


 L&T Exora MCCB DU₹3,799 – ₹6,490
L&T Exora MCCB DU₹3,799 – ₹6,490
-


 Legrand DPX3 MCCB 25kA₹5,056 – ₹20,520
Legrand DPX3 MCCB 25kA₹5,056 – ₹20,520
Working Principle
- Overload Trip
The bimetallic touch overloads the breaker; in normal circumstances, it allows current to flow. It will bend if the current flow crosses the predetermined value, and it will then activate the tripping function. The trip mechanism opens the breaker. Furthermore, since bimetallic contacts take time to return to their original state, the breaker will not reset immediately.
- Short Circuit
An electromagnetic coil provides the breaker’s short circuit safety. The CT produces fewer currents under normal circumstances, so the coil electromagnetic field is insufficient to pull the plunger. The CT produces a high current, and the coil induces a strong magnetic field during fault current or instant fault conditions. As a result, the coil pulls the plunger, tripping the circuit immediately.
- Earth Fault
The safeguard against earth leakage differs from other types of protection. It’s a one-of-a-kind item. It necessitates the installation of additional CT in the molded case circuit breaker.
The existing transformer’s output will be associated with a star pattern. The current flows through the star’s neural point would be zero under ordinary circumstances. If the line leakage is detected, the same will be seen at the start terminal. The MCCB trips the circuit if the leakage flow reaches the permissible limit.
Types of MCCB
The MCCB is classified into five types based on the kinds of tripping:
- Type B
- Type C
- Type D
- Type K
- Type Z
MCCB Rating
The manufacturer offers some technical information that can be used to understand the MCCB’s characteristics better.
Inm – rated Frame current: when the MCCB functions in the stable area, the maximum permissible current through the MCCB.
In => Rated current: The breaker’s responsive tripping range.
Ui => Rated Insulation Voltage: the breaker’s peak allowed voltage ranges.
Ue => Rated Voltage =>The breaker’s operational voltage.
Uimp => Rated Impulse Withstand voltage: The MCCB’s surge voltage is 1.2/50µs, the normal size for impulse checking.
Ics => Short circuit Breaking Capacity: The highest intensity of short-circuit current that the breaker can split without causing physical harm to the circuit.
Ics => Unlimited short circuit breaking capacity: The maximum splitting power of the MCCB, while the MCCB will physically split the circuit. It will not work beyond that point.
Advantages
- Require less room in the electrical box.
- Affordable than ACBs.
- Flexible current settings.
- Low maintenance.
- Fault clearing takes less time than fuse units.
- There’s no need to hold the extras. As a result, the stockpile will be reduced.
- Suitable for both residential and manufacturing use.
Buying MCCB Online
You can quickly browse Ampkart for the appropriate item to help safeguard your electrical appliances.
 (+91) 7439 448 917
(+91) 7439 448 917 Cash on Delivery Available
Cash on Delivery Available



 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Power Distribution
Power Distribution Modular Switchboard
Modular Switchboard Wires & Cables
Wires & Cables