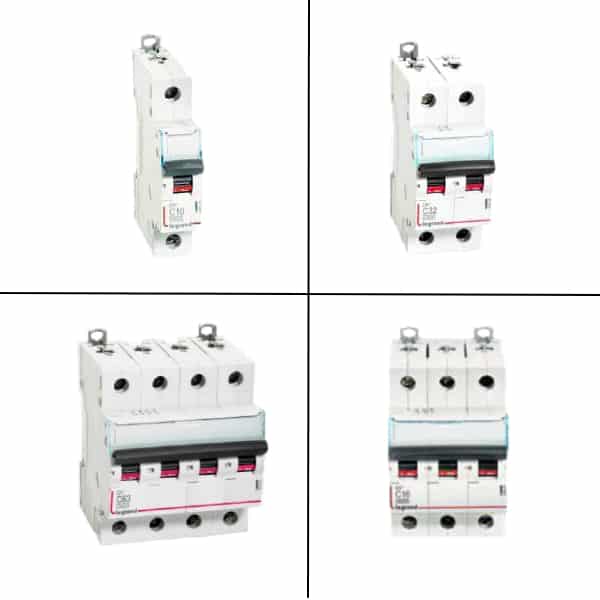
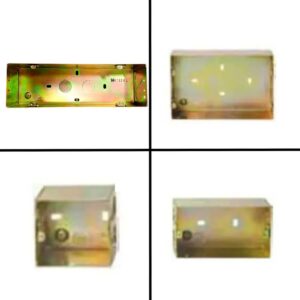
Legrand MCB DX3 C Curve Description
Features and Details:
- 10 kA as per IEC 60947-2
- For AC Applications
- Integrated label holder
- Efficient air channels
- Biconnect lower terminals
- Sliding insulating shield
- Color-coded contact indication window
- IP 20 protected terminals
- 50 sq mm terminals
What is MCB?
A Miniature Circuit Breaker (MCB) is a pivotal component in electrical circuits designed to protect against overcurrents and short circuits. Unlike traditional fuses, MCBs provide a reusable and efficient solution for safeguarding electrical systems.
Ampere Ratings in MCB:
- 6-10A: Suitable for lighting circuits and small appliances like LED bulbs and fans.
- 16A: Suitable for appliances like laptops and refrigerators.
- 20-32A: Ideal for larger appliances and equipment, such as air conditioners and washing machines.
- 40-63A: Used for power heavy appliances like Hot Tubs, Electric Showers, etc.
- 70A-125A: Geared towards heavy-duty industrial applications with substantial loads.
Tripping Curve of an MCB:
The tripping curve of an MCB describes its response time to different levels of overcurrent. It helps determine how quickly the MCB will trip (disconnect the circuit) in response to a fault condition.
- B Curve (General-Purpose): It's commonly used in residential and light commercial applications.
- C Curve (Commercial): It is suitable for protecting circuits with motors, transformers, or other inductive loads.
- D Curve (Industrial): It is suitable for protecting circuits with heavy machinery, large motors, or power distribution networks.
- K Curve (Industrial): The K curve is specifically designed for circuits with high inrush currents.
- Z Curve: This curve is used for sensitive electronic circuits where even small overcurrents can cause damage.
Breaking Capacity (kA) in MCB:
Breaking capacity, often referred to as interrupting capacity, is a crucial specification for MCBs. It indicates the maximum fault current that the MCB can safely interrupt without sustaining damage.
- 3-7 kA: Designed to handle residential and light commercial applications.
- 7-10 kA: commercial and industrial settings
- 10-20 kA: Geared towards heavy industrial applications or heavy machinery with high fault levels.
- 20-100kA: Used in critical applications such as in large industrial facilities or power distribution networks.
 (+91) 7439 448 917
(+91) 7439 448 917 Cash on Delivery Available
Cash on Delivery Available



 Circuit Breakers
Circuit Breakers Power Distribution
Power Distribution Modular Switchboard
Modular Switchboard Wires & Cables
Wires & Cables



















































first class